Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Irisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 591, p.154914_1 - 154914_10, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The amount of corrosion of austenitic stainless-steel R-SUS304ULC was evaluated considering the changes in solution composition and boiling during actual concentration operations. Austenitic stainless-steel R-SUS304ULC is the structural material of the highly radioactive liquid waste concentrator in Japanese spent fuel reprocessing plant, which treats highly corrosive nitric acid solutions during enrichment operations. The study results show that it is necessary to focus on nitric acid concentrations, oxidizing metal ion concentrations, and decompression boiling as factors that accelerate the corrosion rate of stainless steel because of cathodic reaction activation.
Yamashita, Naoki; Aoyama, Takahito; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Tagami, Susumu
JAEA-Technology 2023-028, 22 Pages, 2024/03
At the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), which is currently undergoing decommissioning, there is growing interest in the effects of radiation-emitting radionuclides such as  Sr and
Sr and  Cs on the structural integrity. In particular, the corrosion behavior of carbon steel, which is used in many parts of 1F, is known to change depending on metal cations in solution, but the effects of
Cs on the structural integrity. In particular, the corrosion behavior of carbon steel, which is used in many parts of 1F, is known to change depending on metal cations in solution, but the effects of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs on corrosion are not yet understood. In addition, it is important to investigate the distribution of
Cs on corrosion are not yet understood. In addition, it is important to investigate the distribution of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in the rust layer in order to understand the corrosion behavior, but the method has not yet been established. In this study, a glove box was prepared to conduct corrosion tests of carbon steel in NaCl containing
Cs in the rust layer in order to understand the corrosion behavior, but the method has not yet been established. In this study, a glove box was prepared to conduct corrosion tests of carbon steel in NaCl containing  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in the glove box. In addition, in order to clarify the influence of
Cs in the glove box. In addition, in order to clarify the influence of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs, which exist as metal cations in the solution, on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel, we attempted to establish a detection method for radioactive materials in the rust layer using an imaging plate.
Cs, which exist as metal cations in the solution, on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel, we attempted to establish a detection method for radioactive materials in the rust layer using an imaging plate.
Otani, Kyohei; Kato, Chiaki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Corrosion, 79(11), p.1277 - 1286, 2023/11
Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Uchida, Shunsuke; Lister, D. H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.867 - 880, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)One of the major subjects for evaluating the corrosive conditions in the PWR primary coolant was to determine the optimal hydrogen concentration for mitigating PWSCC without any adverse effects on major structural materials. As suitable procedures for evaluating the corrosive conditions in PWR primary coolant, a couple of procedures, i.e., water radiolysis and ECP analyses, were proposed. The previous article showed the radiolysis calculation in the PWR primary coolant, which was followed by an ECP study here. The ECP analysis, a couple of a mixed potential model and an oxide layer growth model, was developed originally for BWR conditions, which was extended to PWR conditions with adding Li (Na
(Na ) and H
) and H effects on the anodic polarization curves. As a result of comparison of the calculated results with INCA in-pile-loop experiment data as well as other experimental data, it was confirmed that the ECPs calculated with the coupled analyses agreed with the measured within
effects on the anodic polarization curves. As a result of comparison of the calculated results with INCA in-pile-loop experiment data as well as other experimental data, it was confirmed that the ECPs calculated with the coupled analyses agreed with the measured within  100mV discrepancies.
100mV discrepancies.
Yamashita, Naoki; Irisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Tagami, Susumu
JAEA-Technology 2022-035, 29 Pages, 2023/03
In the treatment process of the current commercial reprocessing plant (Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant), the high-level liquid waste concentrator is the equipment that treats the most corrosive solution. In the high-level liquid waste concentrator, the extracted liquid waste after separation of uranium and plutonium is heated, concentrated, and reduced in volume. Therefore, the amount of gamma- rays emitted from fission products and the concentration of corrosive metal ion species such as neptunium-237 ( Np) are the highest in the reprocessing process, and the amount of corrosion in the high-level liquid waste concentrate canner is expected to be large. In this study, in order to clarify the effect of gamma-rays on the corrosion reaction of stainless steel in nitric acid solutions containing
Np) are the highest in the reprocessing process, and the amount of corrosion in the high-level liquid waste concentrate canner is expected to be large. In this study, in order to clarify the effect of gamma-rays on the corrosion reaction of stainless steel in nitric acid solutions containing  Np from the electrochemical viewpoint, the corrosion test apparatus for heat transfer surfaces in an airtight concrete cell at the Waste Safety TEsting Facility (WASTEF) of Nuclear Science Research Institute was modified to enable electrochemical measurements under gamma-ray irradiation. The effect of gamma-rays on the corrosion reaction taking place on the stainless steel surface was discussed from the electrochemical test results obtained. As a result, changes in the immersion potentials of stainless steel and the polarization curves due to chemical species caused by radiolysis of gamma-ray irradiation were confirmed.
Np from the electrochemical viewpoint, the corrosion test apparatus for heat transfer surfaces in an airtight concrete cell at the Waste Safety TEsting Facility (WASTEF) of Nuclear Science Research Institute was modified to enable electrochemical measurements under gamma-ray irradiation. The effect of gamma-rays on the corrosion reaction taking place on the stainless steel surface was discussed from the electrochemical test results obtained. As a result, changes in the immersion potentials of stainless steel and the polarization curves due to chemical species caused by radiolysis of gamma-ray irradiation were confirmed.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Kondo, Keietsu; Fujimura, Yuki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 575, p.154209_1 - 154209_19, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:29.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Previous studies had shown that in certain conditions, the rate of oxidation of zirconium (Zr) based alloy fuel cladding is higher in air-steam mixtures than in dry air. In severe accidents in the spent fuel pool and in other air ingress accidents in nuclear power plants, the cladding is likely to be oxidized in an air-steam mixture, which makes it crucial to have an in-depth understanding of the nature of oxidation and its kinetics in that environment. Oxidation tests were conducted at 800 C on Zircaloy-4 specimens in a mix of (air+steam) with various component ratios. Oxidation kinetics, details of the oxide layer, and hydrogen pick-up in the specimen were studied to investigate the mechanism of oxidation in each of these sets of conditions. Zirconium nitride precipitation in the oxide layer during the initial stages of the pre-breakaway oxidation stage and the widespread porous oxide growth on the cladding surface in the latter post-BA oxidation stage are related to the oxidation mechanism in the air-steam mixture. The differences in the mechanism of oxidation of the cladding in dry air and air-steam mixtures are discussed based on the experimental results.
C on Zircaloy-4 specimens in a mix of (air+steam) with various component ratios. Oxidation kinetics, details of the oxide layer, and hydrogen pick-up in the specimen were studied to investigate the mechanism of oxidation in each of these sets of conditions. Zirconium nitride precipitation in the oxide layer during the initial stages of the pre-breakaway oxidation stage and the widespread porous oxide growth on the cladding surface in the latter post-BA oxidation stage are related to the oxidation mechanism in the air-steam mixture. The differences in the mechanism of oxidation of the cladding in dry air and air-steam mixtures are discussed based on the experimental results.
 to the inside of the crevice by chelation and its effect on crevice corrosion of Type 316L stainless steel
to the inside of the crevice by chelation and its effect on crevice corrosion of Type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Kato, Chiaki
Corrosion Science, 210(2), p.110850_1 - 110850_10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The chelated complex of Cu : [Cu(EDTA)]
: [Cu(EDTA)] was used to introduce Cu
was used to introduce Cu from outside to the inside of crevice. The introduced Cu
from outside to the inside of crevice. The introduced Cu was expected to act as an inhibitor for the crevice corrosion on stainless steels. Crevice corrosion tests, confirmed the introduction of Cu
was expected to act as an inhibitor for the crevice corrosion on stainless steels. Crevice corrosion tests, confirmed the introduction of Cu to the inside of the crevice via electromigration of [Cu(EDTA)]
to the inside of the crevice via electromigration of [Cu(EDTA)] was confirmed. Migrated [Cu(EDTA)]
was confirmed. Migrated [Cu(EDTA)] reacted with H
reacted with H and inhibited decrease in pH inside the crevice, where Cu
and inhibited decrease in pH inside the crevice, where Cu was separated from [Cu(EDTA)]
was separated from [Cu(EDTA)] and suppressed active dissolution of the stainless steel.
and suppressed active dissolution of the stainless steel.
Yamashita, Susumu; Kondo, Nao; Sugawara, Takanori; Monji, Hideaki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 22 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)To confirm the validity of the thermal-hydraulics design tool based on the Ansys Fluent, we used a detailed computational fluid dynamics code named JAEA Utility Program for Interdisciplinary Thermal-hydraulics Engineering and Research (JUPITER) for the thermal-hydraulics around the beam window (BW) of the Accelerator-Driven System (ADS). The Fluent uses the Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) model and can quickly calculate the turbulent flow around the BW as a BW design tool. At first, we compared the results of JUPITER with the experimental results using a mock-up BW system in water to confirm the validity of JUPITER. As a result, we confirmed that numerical results are in good agreement with the experimental results. Thus, we showed that JUPITER could be used as a benchmark code. We also performed a benchmark simulation for the Fluent calculation using validated JUPITER to show the applicability of JUPITER as an alternative of experiments. As a result, the mean values around the BW agreed with each other, e.g., the mean velocity profile for stream and horizontal directions. Therefore, we confirmed that JUPITER showed a good performance in validating the thermal-hydraulics design tool as a fluid dynamics solver. Moreover, Fluent has enough accuracy as a thermal-hydraulics design tool for the ADS.
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Corrosion, 78(6), p.503 - 515, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effects of electrochemical potential (ECP) on water chemistry within a crevice are of critical importance for understanding stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of Fe-Cr-Ni alloys in high temperature water. In this study, the effects of ECP on the electrical conductivity of a solution within a Type-316L stainless steel crevice (
 ) have been studied in 288
) have been studied in 288 C and 8 MPa water containing 10 ppb Cl
C and 8 MPa water containing 10 ppb Cl as major anionic species. In situ measurements of
as major anionic species. In situ measurements of 
 in a rectangular crevice with a gap of 15
in a rectangular crevice with a gap of 15  m and a depth of 23 mm have been conducted using small sensors installed at different crevice depths. An increase in ECP from -0.49 V (vs. standard hydrogen electrode) to -0.12 V resulted in an increase in
m and a depth of 23 mm have been conducted using small sensors installed at different crevice depths. An increase in ECP from -0.49 V (vs. standard hydrogen electrode) to -0.12 V resulted in an increase in 
 from 12
from 12  Scm
Scm to 160
to 160  Scm
Scm at a distance of 21 mm from the crevice mouth. The increase in
at a distance of 21 mm from the crevice mouth. The increase in 
 reached a maximum at about 0.15 V (about 300
reached a maximum at about 0.15 V (about 300  Scm
Scm ) and then tended to decrease with increasing potential. Finite element model analysis taking into account the electrochemical reaction quantitatively reproduced this behavior. It is considered that Cl
) and then tended to decrease with increasing potential. Finite element model analysis taking into account the electrochemical reaction quantitatively reproduced this behavior. It is considered that Cl is the major anionic species transported into the crevice at relatively low potentials, and that
is the major anionic species transported into the crevice at relatively low potentials, and that 
 increases monotonically with increasing ECP. On the other hand, when ECP exceeds around 0 V, a sufficient amount of HCrO
increases monotonically with increasing ECP. On the other hand, when ECP exceeds around 0 V, a sufficient amount of HCrO
 generated by transpassive dissolution also transported into the gap. Since this chemical species is highly oxidizing, unlike Cl, it is assumed that it reacts with metal cations to oxidize and precipitate them, thereby lowering conductivity.
generated by transpassive dissolution also transported into the gap. Since this chemical species is highly oxidizing, unlike Cl, it is assumed that it reacts with metal cations to oxidize and precipitate them, thereby lowering conductivity.
Nagata, Sho*; Miyake, Shugo*; Igarashi, Takahiro; Ota, Hiromichi*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*
Jikken Rikigaku, 22(2), p.105 - 111, 2022/06
Thermal easy axis and thermal diffusivity of uniaxial carbon fiber-reinforced plastic sheets were determined by a offset periodic laser heating method, and investigated relationship between the thermal easy axis and fiber orientation with different thickness of CFRP sheet specimen, experimentally. It was clarified that the orientation of the thermal easy axis spreads in the in-plane direction with the sheet thickness deceases. Then, thermal diffusivity of CFRP specimens in the out-of-plane and in-plane direction were measured by two method: a variable-frequency method and a variable-displacement method, respectively. In the results of the out-of-plane directions, thermal diffusivity almost consistent with the carbon fiber direction were obtained. In contrast, the in-plane directions of those were exhibited unexpected value. Moreover, thermal diffusivity determination by offset periodic heating method was carried out. Finally, it is found that the thermal diffusivity considering the thermal easy axis with fiber angle was different characteristics from the in-plane direction measurement.
Komatsu, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2021-019, 24 Pages, 2022/05
In order to reduce the corrosion rate of materials in molten lead bismuth eutectic (LBE), it is important to adjust the oxygen concentration, and past reports show that the oxygen concentration is often adjusted to about 10 to 10
to 10 wt%. However, it is not clearly stated what concentration is optimal, and there are some reports of severe corrosion even within this concentration range. In this study, a corrosion model considering diffusion in oxide and LBE was developed for 9Cr-1Mo steel, and the corrosion control method estimated from the corrosion model were investigated. We also tried to calculate the optimum oxygen concentration to prevent the flow blockage at the low temperature of loop environment while reducing the corrosion of 9Cr-1Mo steel in molten LBE. As a result, it was expected that the corrosion mode of 9Cr-1Mo steel in LBE could be classified into three types, dense film formation, precipitation film formation, and film dissolution, depending on the ratio of oxide film thickness to diffusion layer thickness, iron concentration in LBE, and temperature. In order to inhibit corrosion, it is important to adjust the oxygen concentration so that the conditions for dense film formation can be maintained. For this purpose, it was expected that a pre-oxidized film of more than 10
wt%. However, it is not clearly stated what concentration is optimal, and there are some reports of severe corrosion even within this concentration range. In this study, a corrosion model considering diffusion in oxide and LBE was developed for 9Cr-1Mo steel, and the corrosion control method estimated from the corrosion model were investigated. We also tried to calculate the optimum oxygen concentration to prevent the flow blockage at the low temperature of loop environment while reducing the corrosion of 9Cr-1Mo steel in molten LBE. As a result, it was expected that the corrosion mode of 9Cr-1Mo steel in LBE could be classified into three types, dense film formation, precipitation film formation, and film dissolution, depending on the ratio of oxide film thickness to diffusion layer thickness, iron concentration in LBE, and temperature. In order to inhibit corrosion, it is important to adjust the oxygen concentration so that the conditions for dense film formation can be maintained. For this purpose, it was expected that a pre-oxidized film of more than 10 m should be applied before immersion in LBE. The oxygen concentration of about 10
m should be applied before immersion in LBE. The oxygen concentration of about 10 to 10
to 10 wt% is the appropriate oxygen concentration when the oxide film has grown to some extent, and a higher oxygen concentration was expected to be required when the film is thin.
wt% is the appropriate oxygen concentration when the oxide film has grown to some extent, and a higher oxygen concentration was expected to be required when the film is thin.
Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(5), p.133 - 137, 2022/05
The effect of the corrosion inhibitor on the corrosion of steel under a thin solution layer was investigated. As a result of forming a thin solution layer with a thickness of 1.0-0.2 mm on the specimen, adding a mixed solution of sodium molybdate and aluminum lactate as a corrosion inhibitor, and performing electrochemical measurement, the corrosion inhibitor suppresses the anodic reaction. And in the thin solution layer, it was suggested that the morphology of the protective layer structure by the corrosion inhibitor changed according to the amount of liquid as compared with the bulk immersion.
Soma, Yasutaka; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo 2022 Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.219 - 220, 2022/05
It is important to understand the electrochemical properties of stainless steel in environment created within crevice of stainless steel in high temperature water (crevice environment). This is because acidification and concentration of impurity ions occur in the crevice environment and this is common inside the stress corrosion crack. In this study, we reproduced the crevice environment in bulk scale and investigated mainly the effect of Cr concentration on the electrochemical properties of Fe-Cr-Ni alloys. Polarization curves of Fe-20Ni-xCr (x=16.4, 23, 26) were measured in water with a temperature of 288 C, a Cl concentration of 2
C, a Cl concentration of 2 10
10 mol/dm
mol/dm , a pH value of about 4.5, and a dissolved hydrogen concentration of 10 ppb. The peak currents of active dissolution (at -400 mV) and passive current density (at -50 mV) for specimens with Cr concentrations x = 16.4, 23, and 26% were approximately 13.8, 15.9, 10.0
, a pH value of about 4.5, and a dissolved hydrogen concentration of 10 ppb. The peak currents of active dissolution (at -400 mV) and passive current density (at -50 mV) for specimens with Cr concentrations x = 16.4, 23, and 26% were approximately 13.8, 15.9, 10.0  Acm
Acm , and 18.4, 8.5, 8.5
, and 18.4, 8.5, 8.5  Acm
Acm , respectively. Although the current values of x=26 were slightly lower in both cases, it was concluded that there was no clear dependence of the polarization curve on Cr concentration in this environment.
, respectively. Although the current values of x=26 were slightly lower in both cases, it was concluded that there was no clear dependence of the polarization curve on Cr concentration in this environment.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Otani, Kyohei; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Bosei Kanri, 66(4), p.141 - 145, 2022/04
Metal corrosion is a material deterioration phenomenon based on electrochemical reactions on an atomic scale. In this paper, various methods for acquiring physical properties on metal surfaces using first-principles calculations were described. As examples of applying first-principles calculation to metal corrosion, the effect of hydrogen adsorption on the metal surface on the potential change and the effect of cation atoms in the aqueous solution on the corrosion resistance of the metal were reported.
Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Abe, Hitoshi
Materials Transactions, 63(4), p.538 - 544, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The time dependence of the corrosion behavior of tantalum (Ta), which is used in nuclear fuel reprocessing equipment, in sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solutions was investigated by immersion tests, and the mechanism of the time dependence was examined via surface observations and electrochemical measurements. The immersion tests were conducted at room temperature with NaOH concentrations ranging from 1 to 7 mol/L for immersion periods of 24 to 168 h. The corrosion rate increased with the NaOH concentration but peaked with the immersion period and then decreased. The time to peak of the corrosion rate was shorter with higher NaOH concentration. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns and Raman spectra of the surfaces of the specimens immersed in the 7 mol/L NaOH solution for more than 48 h showed Na Ta
Ta O
O formation. The polarization resistance decreased with immersion time for all NaOH concentrations up to about 24 h after immersion. Thereafter, the polarization resistance increased with immersion time in 7 mol/L NaOH solution and remained almost constant in the other NaOH concentrations. Findings suggested that the change in the corrosion rate was affected by the film formation during immersion, since the time dependence of the polarization resistance and the sum of film resistance and charge transfer resistance had the same tendencies. The precipitation film was mainly Na
formation. The polarization resistance decreased with immersion time for all NaOH concentrations up to about 24 h after immersion. Thereafter, the polarization resistance increased with immersion time in 7 mol/L NaOH solution and remained almost constant in the other NaOH concentrations. Findings suggested that the change in the corrosion rate was affected by the film formation during immersion, since the time dependence of the polarization resistance and the sum of film resistance and charge transfer resistance had the same tendencies. The precipitation film was mainly Na Ta
Ta O
O formed by the dissolution of the passivity film on Ta.
formed by the dissolution of the passivity film on Ta.
 Sr dissolved solution on corrosion potential of type 316L stainless steel
Sr dissolved solution on corrosion potential of type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(4), p.110 - 115, 2022/04
no abstracts in English
Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(4), p.121 - 125, 2022/04
The effect of solution layer thickness on the atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel was investigated using novel devices fabricated by a 3D printer. These novel devices allowed us to control the solution layer thickness precisely. Potentiodynamic polarization measurements were performed under thickness-controlled solution layer, and oxygen diffusion limiting current density ( ) and anodic current density (
) and anodic current density ( ) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,
) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,  increased and
increased and  decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20
decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20 10
10 cm
cm s
s from the relationship between
from the relationship between  and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
Sugawara, Takanori; Watanabe, Nao; Ono, Ayako; Nishihara, Kenji; Ichihara, Kyoko*; Hanzawa, Kohei*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has investigated an accelerator-driven system (ADS) to transmute minor actinides (MAs) included in high level wastes discharged from nuclear power plants. The ADS is a lead-bismuth cooled tank-type reactor with 800 MW thermal power. It is supposed that the ADS is safer than conventional critical reactors because it is operated in a subcritical state. The previous study performed the transient analyses for the typical ADS accidents such as unprotected loss of flow or beam overpower. It was shown that all calculation cases except loss of heat sink (LOHS) satisfied the no-damage criteria. To avoid the damage by LOHS, the ADS equips Direct Reactor Auxiliary Cooling System (DRACS) to remove the decay heat. The most important points of a DRACS operation are its reliability and to ensure the flowrate in a natural circulation state. This study aims to perform the CFD analysis of the natural circulation to clarify the flowrate in the ADS reactor vessel.
 Np
NpIrisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki; Yamashita, Naoki; Sano, Naruto
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(3), p.70 - 74, 2022/03
In order to evaluate the corrosion of stainless steels used in spent nuclear fuel reprocessing facilities, the immersion corrosion tests and polarization measurements were performed using R-SUS304ULC stainless steel in nitric acid solution containing a kind of radionuclides,  Np. At temperatures above 328 K, the corrosion potential was higher than that in nitric acid solution and was near the transpassive region. From the comparison between the corrosion amount calculated by the immersion corrosion tests and the polarization resistance, the values of
Np. At temperatures above 328 K, the corrosion potential was higher than that in nitric acid solution and was near the transpassive region. From the comparison between the corrosion amount calculated by the immersion corrosion tests and the polarization resistance, the values of  =0.018-0.025 V were obtained as a conversion factor, and the possibility of calculating the corrosion amount from the electrochemical measurement was examined.
=0.018-0.025 V were obtained as a conversion factor, and the possibility of calculating the corrosion amount from the electrochemical measurement was examined.
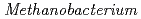 strain induces severe corrosion by retrieving electrons from Fe
strain induces severe corrosion by retrieving electrons from Fe under a freshwater environment
under a freshwater environmentHirano, Shinichi*; Ihara, Sota*; Wakai, Satoshi*; Dotsuta, Yuma; Otani, Kyohei; Kitagaki, Toru; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
Microorganisms (Internet), 10(2), p.270_1 - 270_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:78.86(Microbiology)To understand the role of methanogens in corrosion under anoxic conditions in freshwater, we investigated the corrosion activities of methanogens in samples collected from groundwater and rivers. We enriched microorganisms that can grow with CO /NaHCO
/NaHCO and Fe
and Fe as the sole carbon source and electron donor, respectively, in ground fresh water. Electrochemical analysis revealed that
as the sole carbon source and electron donor, respectively, in ground fresh water. Electrochemical analysis revealed that 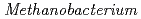 strain can uptake electrons from the cathode at lower than -0.61 V vs SHE and has a redox-active component with electrochemical potential different from those of other previously reported methanogens with extracellular electron transfer ability. This study indicated the corrosion risk by methanogens capable of taking up electrons from Fe
strain can uptake electrons from the cathode at lower than -0.61 V vs SHE and has a redox-active component with electrochemical potential different from those of other previously reported methanogens with extracellular electron transfer ability. This study indicated the corrosion risk by methanogens capable of taking up electrons from Fe in anoxic freshwater environments and the necessity of understanding the corrosion mechanism to contribute to risk diagnosis.
in anoxic freshwater environments and the necessity of understanding the corrosion mechanism to contribute to risk diagnosis.